# Overview
The GIPSIE® software is capable of simulating arbitrary digital intermediate frequency (IF) GNSS signals. The sampled signal is available as digital file, which can be upconverted to RF and replayed by a proprietary hardware simulator.
The schema depicts the possible inputs that are required and the outputs that are produced by GIPSIE RTX. Furthermore, optional inputs are:
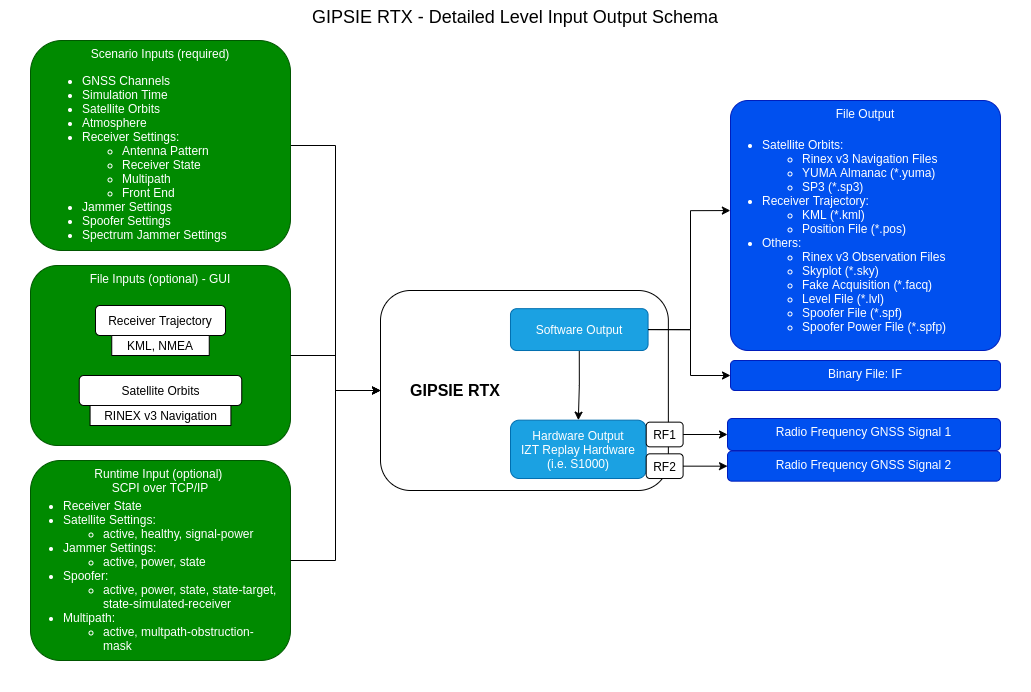
- file imports via the GUI (i.e. for the receiver trajectory or satellite ephemeris)
- SCPI commands via TCP/IP interface to change scenario parameters during the simulation (i.e. change which satellites are actively simulated)
The output of GIPSIE RTX is either a binary file output in IF (IF mode) or the signal is immediately replayed as RF (RF mode) by the S1000 hardware antenna channels RF1 and RF2. Additionally, several intermediate files, such as RINEX observation and navigation and receiver trajectory files are produced for each scenario computed.
IF mode
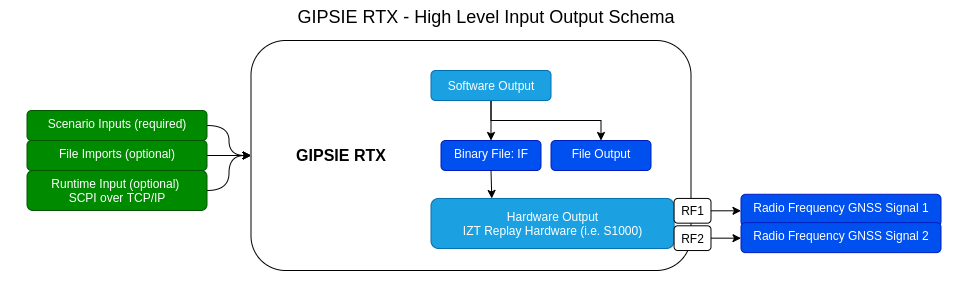
RF mode
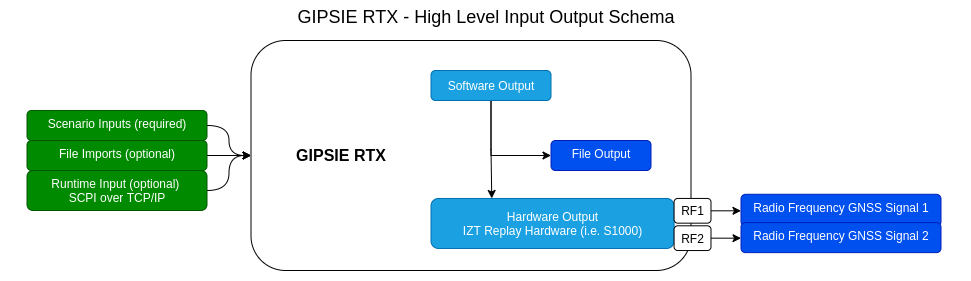
A more detailed schema of all input and output parameters is depicted in the image below.
Detailed Input/Output Schema
# Simulation Aspects
The software is capable of simulating different aspects of a navigation signal and these aspects directly refer to the main options available in the software.
# GNSS Channels
Depending on the GNSS, several channels can be selected to be simulated for a scenario.
# Time Settings
The simulation time can be set from a variety of different time systems and is automatically transferred to other time-systems.
# Satellites
Satellite Orbits:
two options are available- Ephemeris parameters are used to compute the satellites orbits
- Runge Kutta orbit integration, including perturbing forces of sun and moon; computation of orbital elements for the navigation message from the integrated orbits
Satellite Clocks: simulation of quadratic polynomials, randomized for each satellite and adding noise which is based on the different types of atomic clocks, and computed with respect to their spectral noise behavior (Allan deviation)
# Atmosphere
- Ionosphere: use of NeQuick Galileo and Klobuchar models and derivation of the navigation message parameters; Ionospheric activity can be set also by sunspot number
- Troposphere: use of Galileo user reference, Global Temperature and Pressure 2 wet (GPT2w), Hopfield troposphere models
# Receiver
- Receiver Trajectories: definition of waypoints for receiver trajectories; input through waypoints and calculation with first and second geodetic principals on the ellipsoid with arbitrary height profiles
- Front-End settings: detailed configuration of several front-ends possible
- Antenna Pattern: definition of elevation masks and antenna gain patterns; the signal attenuation is computed based on the geometric relation as well as the use of user selected receiver antenna profiles and modelled satellite antenna patterns.
# Local Environment
- Multipath: simulation of multipath environments based on statistical model
- Interference: simulation of an arbitrary number of interference signals with userdefined signal parameters
- Spoofing: advanced spoofing signal simulation including modelling of imperfect alignment as well as multiple spoofing signal capabilities
# Signals
GIPSIE® is able to simulate global and regional navigation satellite system signals (see the list of available signals).
